Binary Search Trees
A binary search tree (BST) is a tree data structure set up to make binary search efficient.
Characteristics of Binary Search Trees
The root node of a binary search tree has all of the following:
- The left node is less than the root node.
- The right node is greater than the root node.
- Each subtree is a binary search tree.
Empty trees are binary search trees.
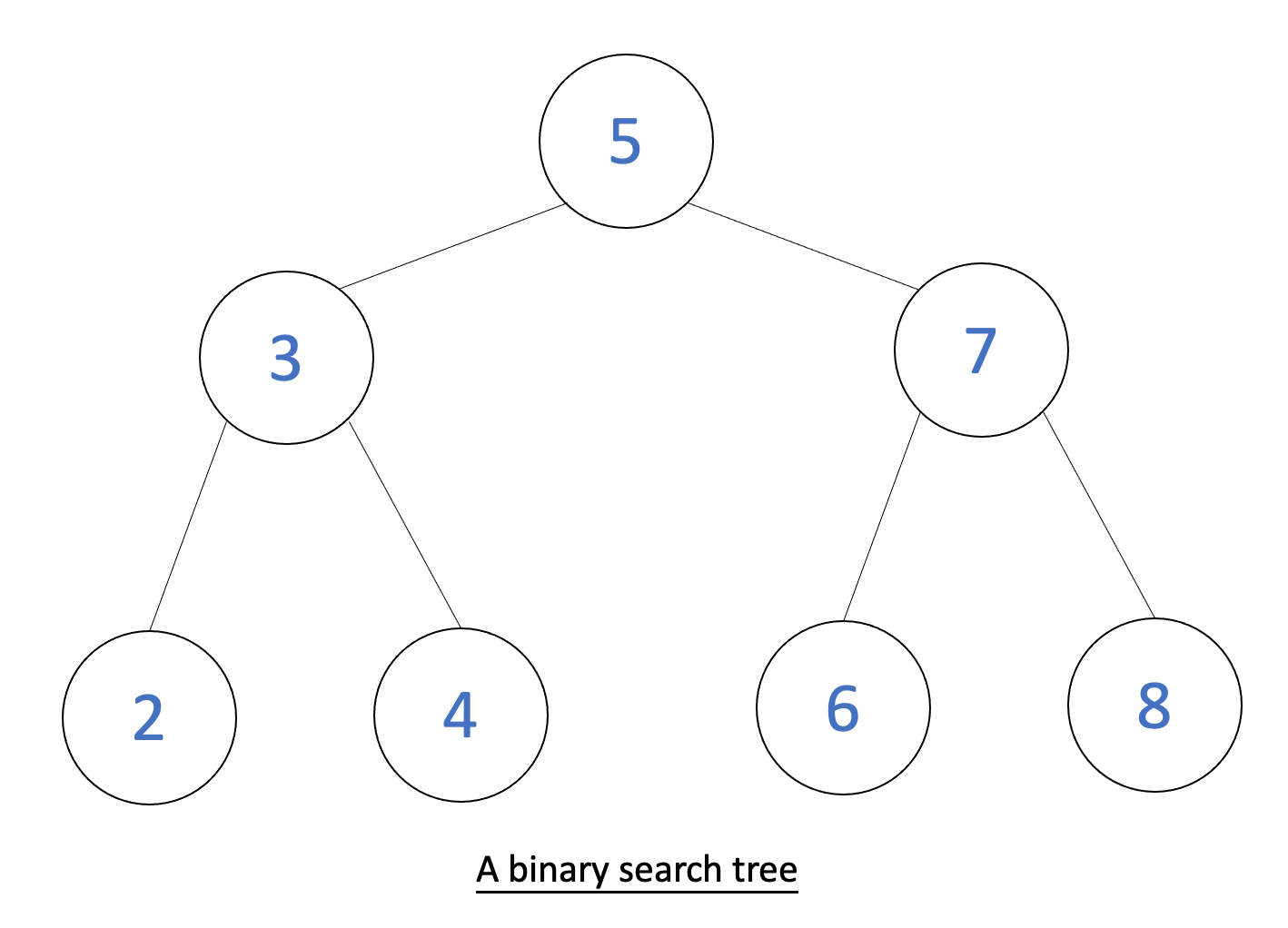
Example Binary Search Tree
Below is a picture of a BST:
Binary Search Tree Functions
Here are example algorithms for search and insert functions.
Search Function
Here is the algorithm to determine if a number is in a binary search tree:
- Pass the root node and the number to search for into the function.
- If the node is NULL, return False.
- If the number is the node, return True.
- If the number is less than the node, search the left node.
- If the number is greater than the node, search the right node.
Insert Node Function
Here is the algorithm to insert a number into a binary search tree:
- Pass the root node and the number to insert into the function.
- If the node is NULL, return a new node that stores the number.
- If the number is less than the node, call the insert function on the left node.
- If the number is greater than the node, call the insert function on the right node.
- Return the root node when all is said and done.
This function always inserts new nodes at leaf nodes.
Time Complexity
Here are the time complexities for searching, inserting into, or deleting from a binary search tree:
Average time complexity: \(O(log \ n)\)
Worst-case time complexity: \(O(n)\)
More Resources
Below are some more resources to learn about binary search trees: