Binary Search
Binary search looks up an item in a sorted array by dividing the search space by 2 until the item is found.
How Binary Search Works
Binary search has a few steps. Here’s how it works:
First, before you start, make sure you are using a sorted array. Binary search needs the array to be sorted for it to work effectively.
Steps:
- Find the lowest index and highest index in the array.
- Find the middle element’s index using this formula: \(midIndex = \frac{lowIndex \ + \ highIndex}{2}\)
- If the middle index points to the number we’re looking for, return the middle index.
- If the number at the middle index is larger than the number we’re looking for, use this formula: \(highIndex = midIndex - 1\)
We only want to search through the numbers less than the middle index. - If the number at the middle index is smaller than the number we’re looking for, use this formula: \(lowIndex = midIndex + 1\)
This way we only search through numbers larger than the number in the middle. - Repeat steps 2 through 5 until the middle index points to the number we’re looking for.
Example
Here’s a sorted array:
Let’s find the number 8 using binary search. Find the low, high, and middle index.
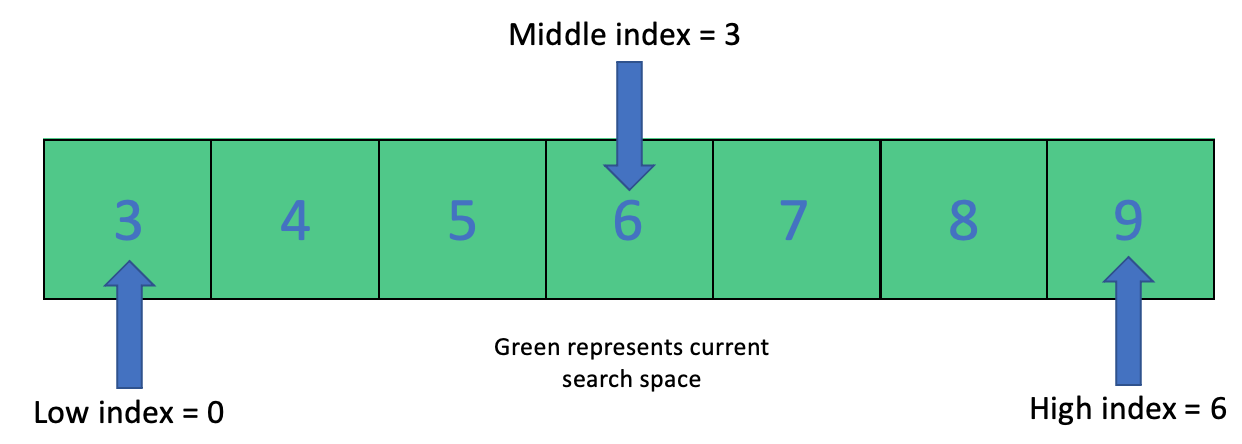
Because \(8 > 6\), we move the low index up so that it points to 7.
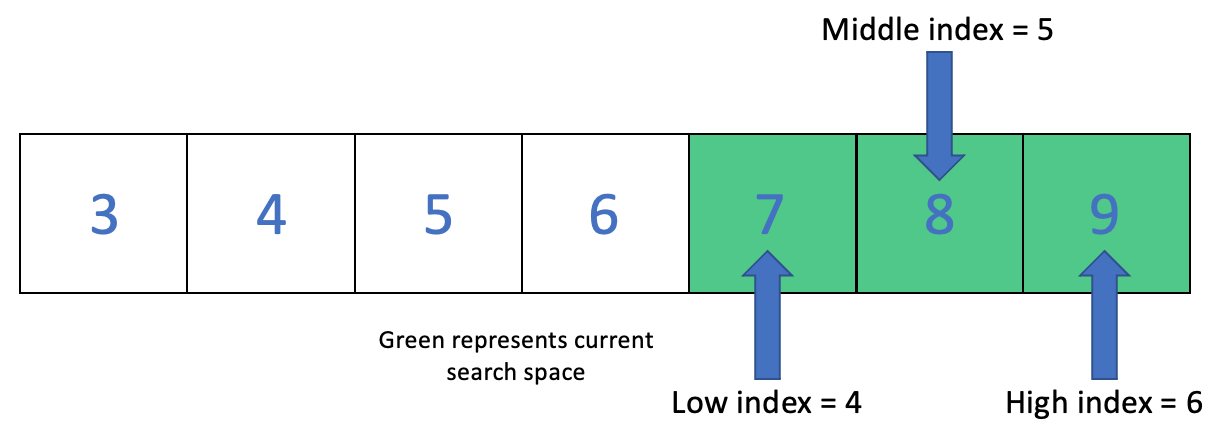
Then we check what the middle index points to, and it points to 8.
The index we are looking for is 5.
Time Complexity
Best case time complexity: \(O(1)\)
This happens when the number we’re looking for lands directly in the middle of the array.
Average time complexity: \(O(log \ n)\)
Worst case time complexity: \(O(log \ n)\)
More Resources
Below are some more resources to learn about binary search: